A while ago, TIA-Celestia, this modular public chain was extremely popular, so much so that when I looked at it, I thought that $1 was a reasonable range. I didn't expect it to reach nearly $20 at its peak, and what it is most famous for is its DA. Later, we talked about some projects that all used DA from Celestia. So what is this DA? Let's explain it.
Components of a modular blockchain:
- Execution layer: Including Rollup, L2 (Layer 2), L3 (Layer 3), the part that executes user/smart contract calculations, similar to a computer.
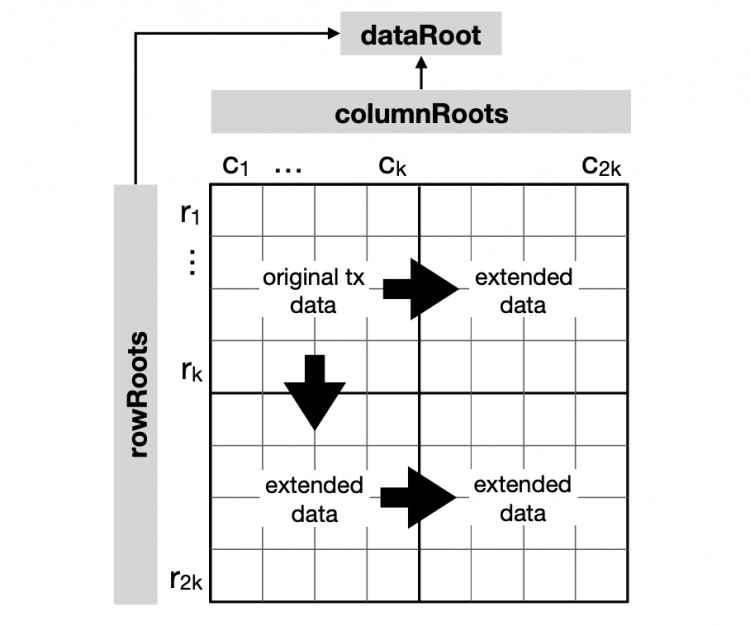
- Data storage layer (DA): All original transactions of the execution layer are stored here for subsequent verification and confirmation, similar to a database.
- Settlement/Settlement: Responsible for verification, confirmation and final confirmation. Users can initiate rebuttals here, using the original execution layer data stored in DA.
- Consensus layer: Mainly the content of Layer 1, which is not described in detail here.

2. Main technology stack or representative products of the three levels:
- Execution layer:
- OP Stack
- ZK Stack
- Cosmos Stack
- Settlement:
- Eth layer1
- Dymension (a settlement in collaboration with Celestia)
- Layer2 itself (such as Arbitrum, which can serve as a settlement for the secondary layer 3)
- DA:
- ETH blob/Danksharding
- Celestia
- Near DA
- Centralized DA (Validum model)
3. How modular blockchains fit together:
- The above creates 45 possible combinations, such as:
- Mantle: OP + ETH L1 + MantleDA
- XAI: OP + Arbitrum L2 + Third-party DA
4. Security differences in different modes:
- In addition to cost and TPS, Ethereum maintains "orthodoxy", Vitalik believes that only DA using Ethereum can guarantee the safe withdrawal of assets. Other solutions are collectively referred to as "Validum". According to the "short board theory", the security is the minimum when settling on Ethereum but using other DA.
5. Future settlement layer:
- It is predicted that there will be 2-3 major settlement layers, and cross-chain assets across settlement layers are still a challenge. Interoperability issues need to be resolved.
6. Future DA layer:
- It is expected that the DA layer will be decentralized, and DA will take various forms. The decentralization of sampling patterns may be affected by network effects. There may be 7-8 major DAs in the future.
7. Impact on the Narrative of Aether:
- If the DA layer becomes fragmented in the future, it may be disadvantageous to Ethereum, but Ethereum's advantage lies in devouring the high-end market. Ethereum's future narrative may focus on L2 interoperability, which is an area that other public chains find hard to compete with. Interoperability is expected to bring value capture, similar to the concept of the ATOM 2.0 whitepaper.
